Group dynamics
Group dynamics is defined as the behavior of a group of people under certain circumstances, and the way they transform with the circumstances.
Concept:
It is concerned with the interaction of forces among group members in a social situation. Group dynamics contains two terms: group and dynamics. Group is basically a bunch of two or more folks. Dynamics comes from Greek word Force. It was founded by Kurt Lewin to study group decision, group productivity, group interaction, and communication.
Nature:
- It can be described as behavioral features of a group.
- It is concerned with the formation of the group, the structure of the group, and the functional process of the group.
- Group dynamics are viewed from the perspectives of the internal nature of groups, how they form, their structure and processes, and how they function and affect individual members, other group and the organization.
and Importance:
- Security
- Status
- Self-Esteem
- Affiliation
- Power
- Goal Achievement
- Socialization of New Employees
- Getting the Job Done
- Decision Making
- Communication
Group formation:
- Two or more individuals can form a group.
- Interacting and interdependent with each others.
- Perceive themselves as members of the group.
- Come together to achieve particular shared objectives and goals to achieve.
- People have similar interest of strive to solve problems together.
Characteristics:
They are listed below:
- Collection of people
- Interaction and Interdependence
- Similar interest
- Common goals
- Role Differentiation
- Functions: Organizational and Psychological.
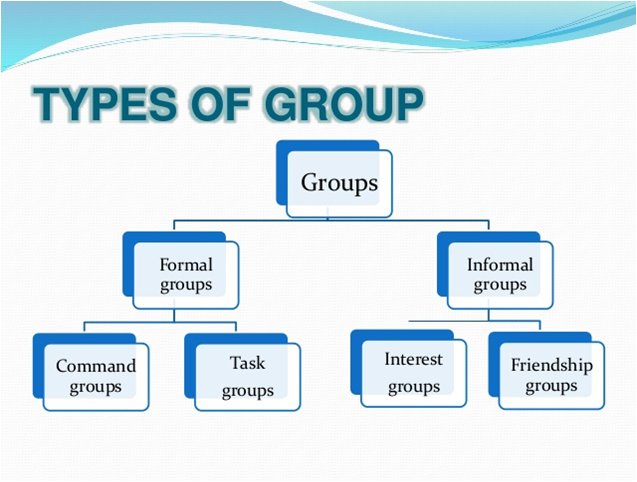
Types of groups:
Stages of group development:
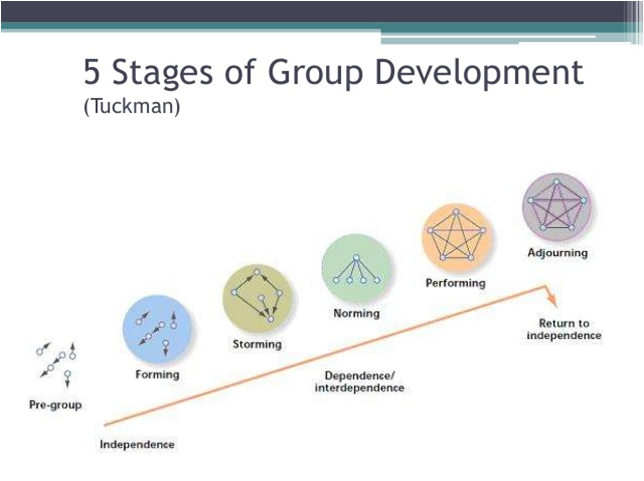
- Forming: members join and begin the process of defining the group’s purpose, structure and leadership.
- Storming: Intragroup conflict occurs as individual resist control by the group and disagree over leadership.
- Norming: Close relationships develop as the group becomes cohesive and establishes its norms for acceptable behavior.
- Performing: A fully functional group structure allows the group to focus on performing the task at hand.
- Adjourning: The group prepares to disband and is no longer concerned with high levels of performance.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GROUP AND TEAM are listed below:
| GROUP | TEAM |
| Goal is to share information | Goal is collective performance |
| Negative synergy or neutral | Positive synergy |
| Strong and focused leader | Shared leadership roles |
| Individual accountability | Individual and team accountability |
| Rewards are member based | Rewards are team based |
| The member skills are random and varied | The member skills are multiple and complementary |
You may also like Leadership || Motivation and Leadership || Organizational Behavior.

Leave a Reply