
Motivation:
Motivation in OB means inspiring the personnel with zeal to do work for the accomplishment of the objective of the organization. Motivation in OB represents those psychological processes that cause the arousal, direction, and persistence of voluntary actions that are goal-directed.
Concept:
The term motivation in OB is derived from the Latin word “movere” ‘which means to move’ and is derived from the word ‘motive’. In general, it is the will to work. It is a difficult factor to manage by the managers.
Nature of characteristics of motivation:
- internal feeling; basically a psychological process
- produces goal-directed behavior
- can be either positive or negative
- motivation contains system orientation.
Importance of Motivation in OB:
The level of performance of an employee is a function of his attitudes, motivation, and opportunity to do.
P=f(A+M+OD)
Process of motivation:
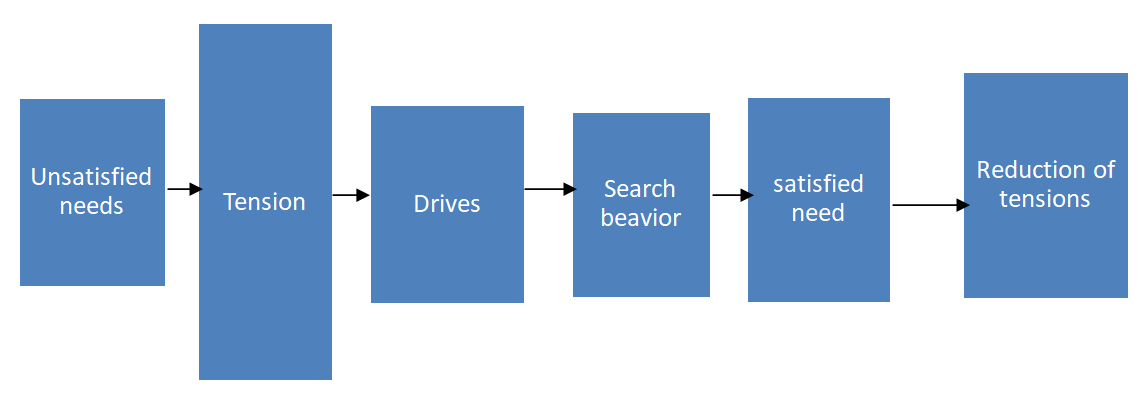
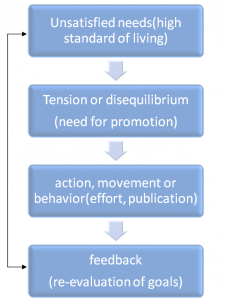
Theories of motivation in OB:
- Content theories of motivation: Maslow’s Need hierarchy theory, Herzberg’s two-factor theory, and Alderfer’s ERG theory.
- Process theories of motivation: Expectancy theory, Equity theory.
A. Content theories of motivation:
Maslow’s Need hierarchy theory:
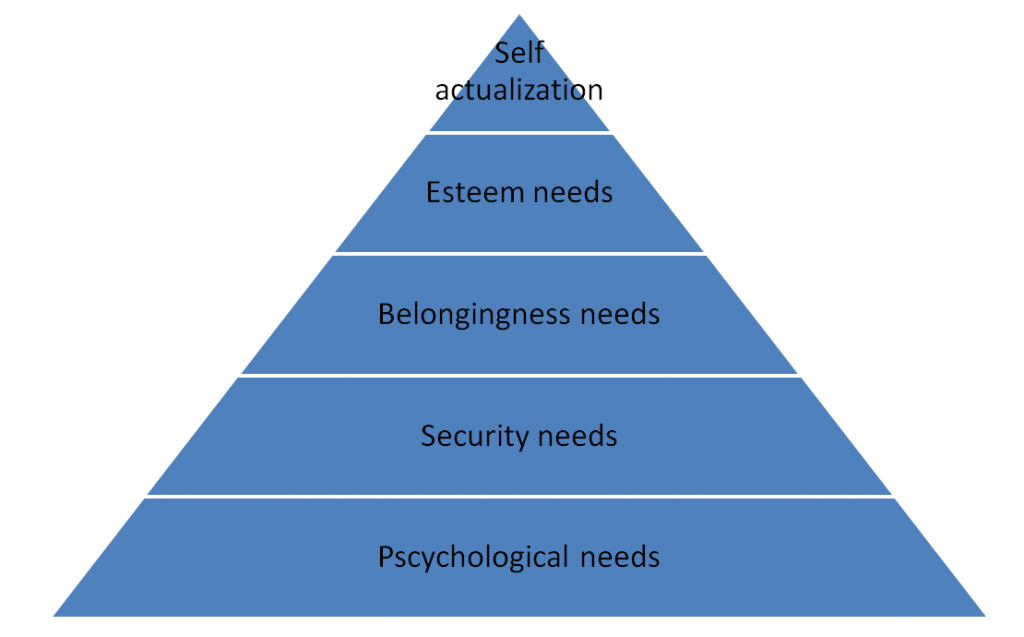
Herzberg’s two-factor theory:
called dual-factor theory of motivation. He extended the work of Maslow and developed a scientific content theory of work motivation.
| Extrinsic(hygiene/maintenance | Intrinsic(motivators/satisfier) |
| Company policy and administration | Achievement |
| Relationship with supervisor | Recognition |
| Work conditions | Work itself |
| Salary, responsibility with others | Responsibility |
| Personal life | Advancement |
Elderfer’s ERG theory:
Clayton Alderfer extends Maslow’s theory and Herzberg’s theory. He formulated a need category model that was more in line with the existing empirical evidence. Similarly, he feels that there is value in categorizing needs and there is a basic distinction between lower and higher-order needs.
- Existence needs Those necessary for basic human survival- roughly compared to the psychological and security needs of Maslow’s hierarchy.
- Relatedness needs: Those involving the need to relate to others, are similar to Maslow’s hierarchy.
- Growth needs: are analogous to Maslow’s needs for self-esteem and self-actualization
2. Process theories of motivation in OB:
Expectancy theory:
Equity theory:
Comparison of self with others based on inequity and equity:
| Equity | Inequity |
| Motivation to maintain the current situation
|
Motivation to reduce inequity:
|
You can also check other similar contents of OB as:
Learning and Behavior || Perception, Personality, and Learning.

Leave a Reply