
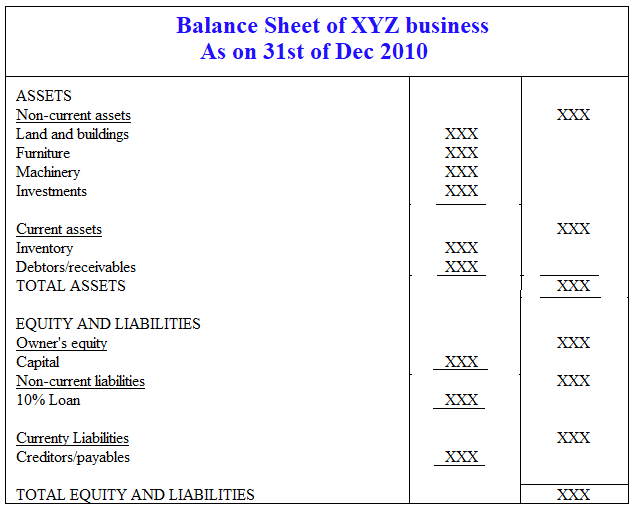
Preparation of balance sheet under vertical- classified format
A vertical balance sheet is one in which the balance sheet presentation format is a single column of numbers, beginning with asset line items, followed by liability line items, and ending with shareholders’ equity line items. Within each of these categories, line items are presented in decreasing order of liquidity. Vertical analysis is the comparison of various line items within a single period. It compares each line item to the total and calculates the percentage of the line item is of the total. It can be done with the company’s Financial Statements or with the use of the Common Size Statements.
Thus, the presentation within the topmost block of line items (for assets) begins with cash and usually ends with fixed assets (which are much less liquid than cash) or goodwill. Similarly, the liabilities section begins with accounts payable and usually ends with long-term debt, for the same reason.
The Difference Between a Vertical and Horizontal Balance Sheet
The only alternative to the vertical balance sheet format is the horizontal balance sheet, where assets appear in the first column and liabilities and shareholders’ equity appear in the second column. In this format, the totals of each column should always be the same.
The vertical balance sheet format is much more popular than the horizontal balance sheet format because you can use it to include the balance sheets for multiple periods on a single page, using a side-by-side presentation format that may span a large number of reporting periods.
Assets Side of Balance Sheet
An asset is a resource legally owned by the enterprise as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise. Assets may be classified as current assets, investment, fixed assets, and other assets.
- Current Assets
- Investments
- Property, Plant & Equipment/Fixed assets
- Intangibles
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity Side of Balance Sheet
- Current liabilities
- Long-term debt
- Deferred income taxes
- Common stock and preferred stock
- Additional paid-in-capital
- Retained earnings
- Treasury stock
You may also like Assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity

Leave a Reply