
Leadership
Concept of Leadership:
Leadership is defined as influence that is, the art or the process of influencing people to that they will strive willingly towards the gaining of group goals. In general it is basically an art of inspiring and influencing the subordinates so that they work hard and corporate enthusiastically in the achievement of group goals.
STEPHEN P. ROBBINS “ Leadership is the ability to influence a group towards achievement of goals.”
Functions of a leader:
- Representative of followers
- Develops team work and motivates them
- manages the resources properly
- It is a human factor- an art, an ability and many more as a part of management.
Leadership styles:
- Autocratic style
- Democratic style or Group-centered
- Free Rein Style or Laissez-faire
| Autocratic style (leader centered) | Democratic style(equal focus) | Free Rein Style or Laissez-faire(follower centered) |
Nature:
|
Nature:
|
Nature:
|
Advantages:
|
Advantages:
|
Advantages:
|
Disadvantages:
|
Disadvantages:
|
Disadvantages:
|
Leadership theories:
- trait theory,
- behavioral theory,
- Fielder’s contingency theory,
- Managerial Grid,
- Path-Goal theory
A. Trait theory:
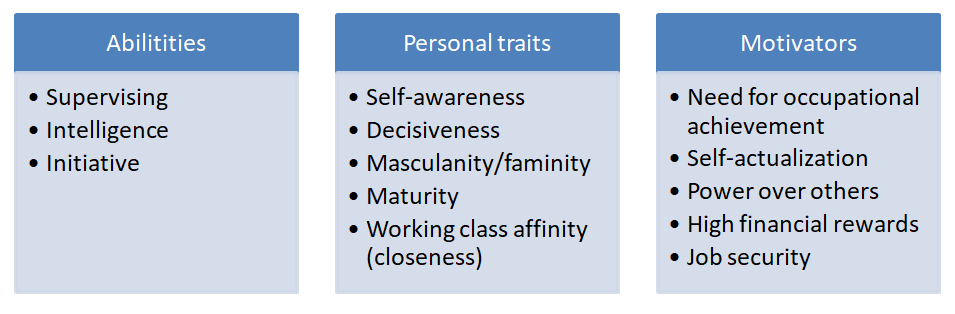
It is the oldest approach which dominated the field of leadership till 1940s. It argues that leadership is largely a matter of personality, a function of specific traits. Differentiates leaders from non-leaders. This approach assumes that ‘leaders are born, not made’. To be a leader a person must possess certain qualities. But in fact there is no scientific prove on this theory.
Traits can be:
- Personality oriented
- Social oriented
- Physical oriented
- Intellectual oriented
Basic assumptions:
- by birth leaders receive leadership traits
- differ greatly from their followers
- traits remain unchanged across time
Behavioral theory (late 1940s to 1960s) :
It is based on the premise that effective leadership is the result of effective role behavior. Success of leadership depends more on what the leader does than on his/her unique traits. The leadership effectiveness is determined in terms of how leaders delegate their tasks, how they communicate with and motivate their followers.
Categories of Behavioral theory:
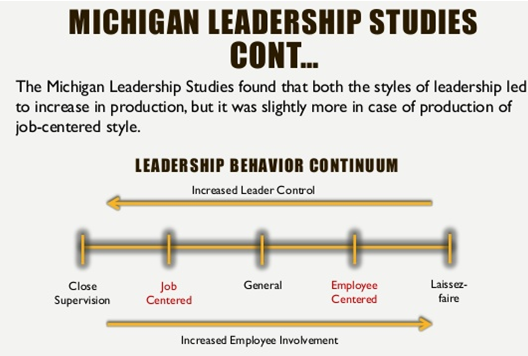
- The Michigan Studies
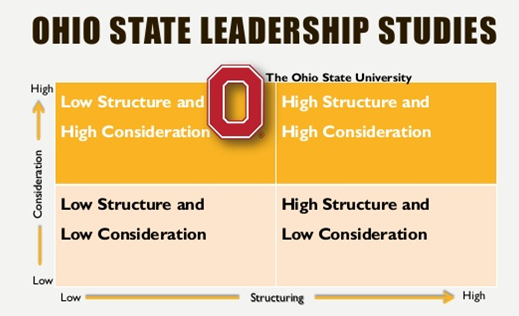
- The Ohio State Studies
- Managerial Grid
| The Michigan Studies: | The Ohio State Studies | Managerial Grid |
Basic assumptions:
|
Basic assumptions:
Thus, high-structure and high-consideration style tended to achieve subordinate performance and more satisfaction than other combination leaders.
|
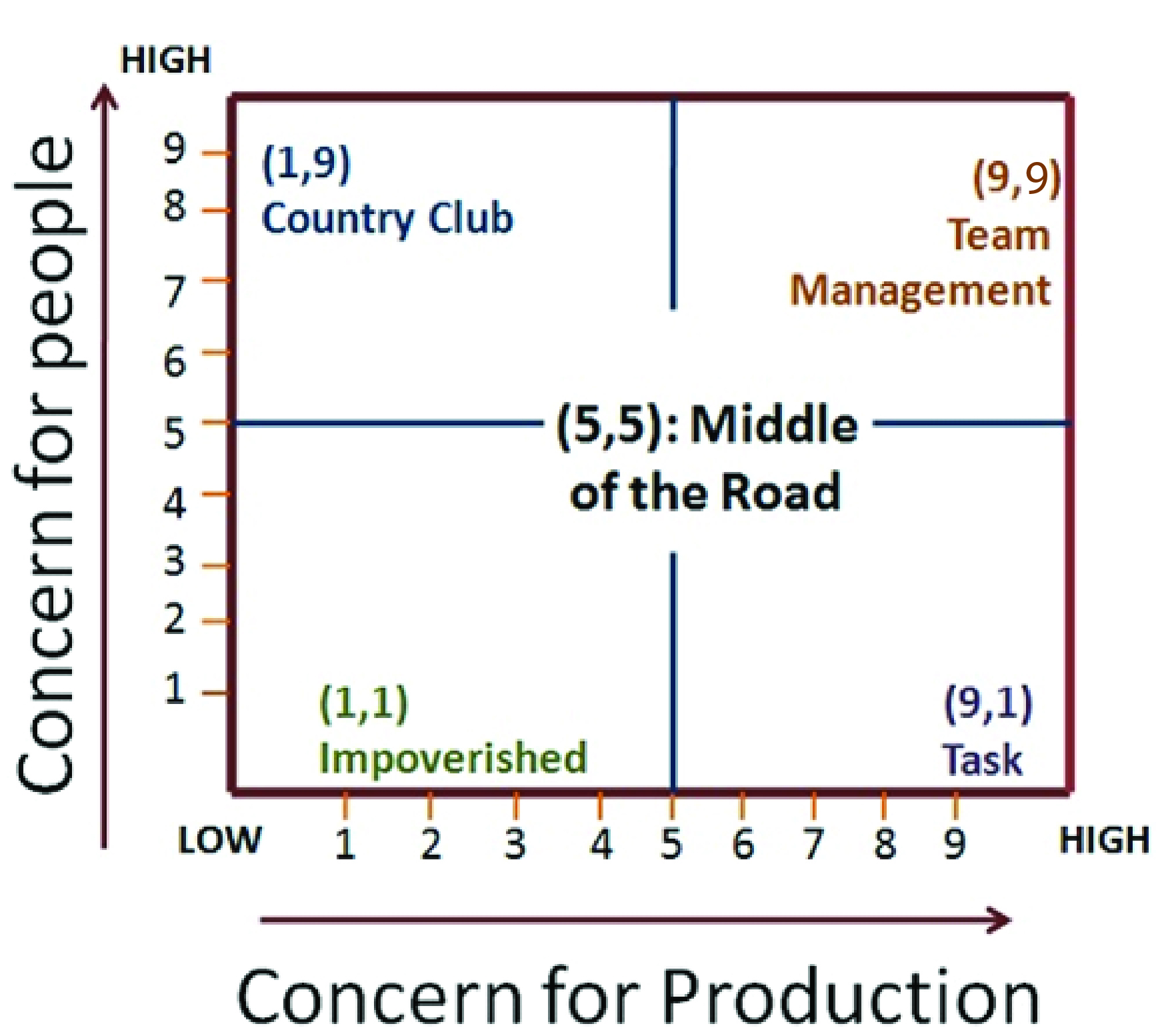
Basic assumptions: The managerial grid has two dimensions:
The grid is 9*9 matrix different styles of leadership. Five important styles of leadership advocated by Grid approach are explained by help of figure :
|
| Employee centered leader
Objective: build effective work groups with high performance goals. Behaviors:
|
Initiating structure:
|
|
|
Production centered leader: Objective: Effective competition of task. Behaviors:
|
Consideration:
|
Contributions:
|
Fielder’s contingency theory(SITUATIONAL APPROACH):
- It states “nature of situation affects leadership.”
- Leader behavior should fit with situation demand .
- Leadership should be situational.
- No universally applicable leader behavior.
There is no one best style of leadership universally applicable to all situations.
If asked to describe the person on a series of bipolar objective scale as given below:
| Friendly 8 7 6 5 4 3 3 1 unfriendly |
| Enthusiastic 8 7 6 5 4 3 3 1 unenthusiastic |
| Cooperative 8 7 6 5 4 3 3 1 uncooperative |
Two main styles of leadership by Fred’s:
- Human relations style
- Task directed style
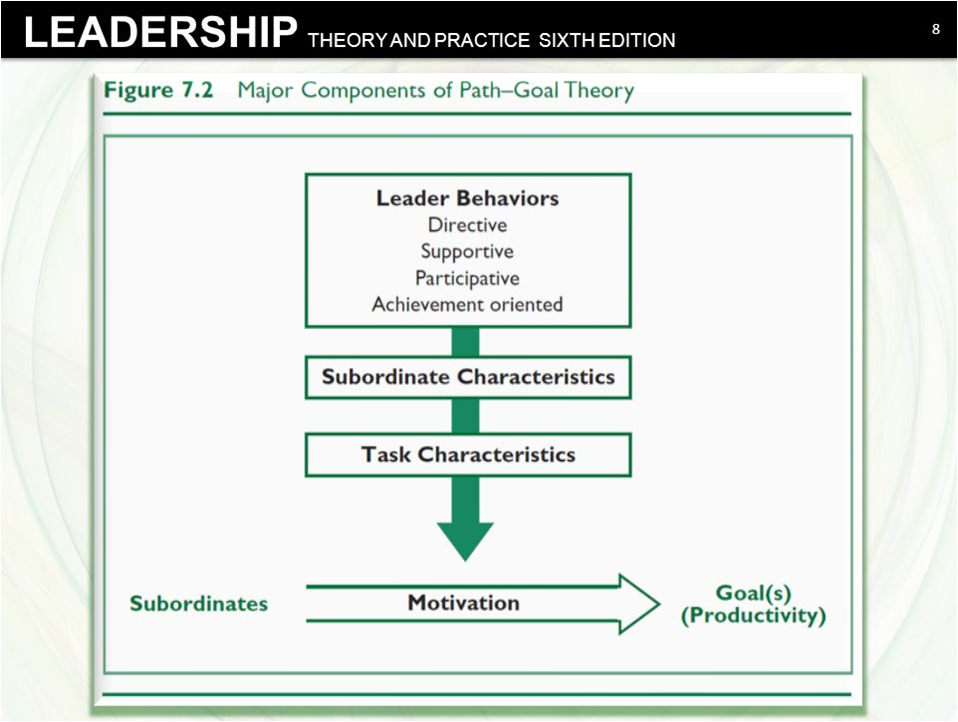
Path-Goal theory:
It was developed by R.J. House and Martin Evans. This theory is based on the expectancy the0ry of motivation.
- It describes what leaders must do to motivate people to perform well and to get satisfied from their work. The leaders should be able to provide the subordinates with the information, support and other resources and help them to achieve their goals.
- The essence of this theory is that it is the leader’s job to assist subordinates attain their goals and to provide the necessary direction or support. It has emphasized on effective leadership styles to clarify the path and help the subordinates to achieve their goal and make journey easier by reducing the obstacles.
Emerging issues in leadership:
- Leadership through empowerment
- Cross-Culture
- Cultural Issues
- Gender Issues
- Team Leadership Issue
- Emotional Intelligence
- Ethical Leadership
You may also like Personality || Perception, Personality and Learning.


Leave a Reply