Understanding Individual Behavior
Concept of Individual behavior : Individual behavior is caused, motivated and goal oriented. Every individual is different from their birth even in twins closer observation may needed but, we can find distinct and unique instincts, reflexes and personal abilities. To understand the root problem of the organization, a thorough study of individual behavior plays a vital role.
Soon after the birth, a person is affected by the environmental variables. The inherited characteristics is converted into learning experience to a complete personality. Heredity and environment are so closely linked together that it is impossible to isolate the effect of one on any one another in developing and moulding individual. It is a long search of a man in quest of finding himself.
Psychologist Kurt Lewin has conducted considerable research into the human belief and proved that behavior is affected by the number of both genetic and environmental factors.
B=f(P,E)
where B=individual behavior
P=Person
E= Environment around him
The table shows what includes in the person and in the environment in the context of human behavior:
The person |
The environment |
| 1. Personal factors:
a. Sex b. Age c. Education d. Abilities e. Marital status |
1. Environment factors:
a. Economic conditions b. political situations c. Cultural values, and d. Social norms |
| 2. Psychological factors
a. Personality b. Perception c. Attitudes d. Values, and e. Learning. |
2. Organizational factors
a. Physical facilities b. Organizational structure c. Organizational design d. Leadership styles, and e. Reward system. |
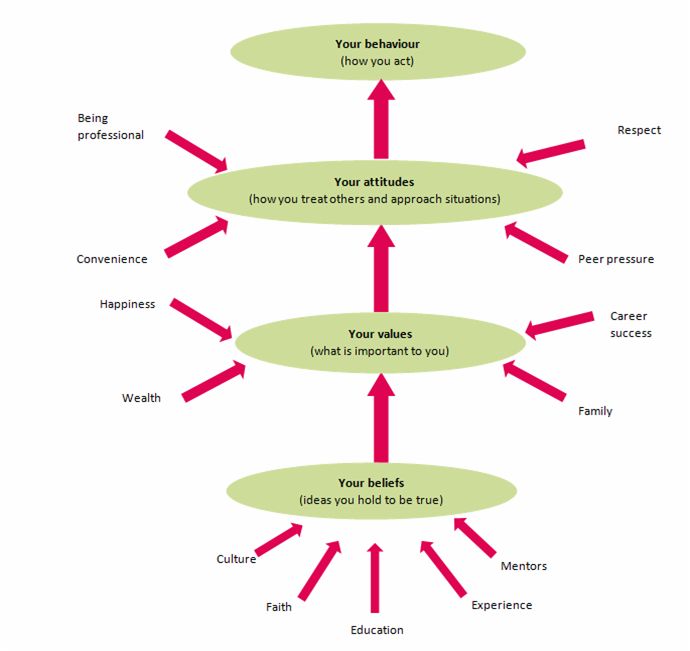
DETERMINANTS OF IINDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR:
- Goals
- Beliefs
- Attitudes
- Values
- Emotions
- Motives
- Behavior
- The relationship between needs, motives and behavior
Goals:
All individuals are goal oriented and they pay their physical and mental efforts to get the specified goal. Goal setting clarifies the intentions of individual to achieve the goal which obviously shape our actions.
| Why do we need to study individual goals? |
| Goals are ultimate objectives that employees want to achieve with their efforts. |
| they are useful to provide useful tools to manage motivation, and to use them as a controlling mechanism for managing work in the organization |
| It helps to focus employees attention on items of greater importance and stimulates them towards goal attachment. |
| managers should set goals for an organization as well as for a individual employee. |
2. Beliefs
What are beliefs?
Beliefs are cognitions, or thoughts, about the characteristics of objects. Attitudes are a result of beliefs.
- It is an internal feeling that something is true, even though that may be unproven or irrational.
- Belief shape our values, impact our emotions and motivates behavior.
- A person can base a belief upon certainties (e.g. mathematical principles), probabilities or matters of faith.
- A belief can come from different sources, including:
– A person’s own experiences or experiments
– The acceptance of cultural and societal norms (e.g. religion)
– What other people say (e.g. education or mentoring).
| Why do we need to study beliefs? |
| Beliefs provide continuity to the personality of an individual. |
| It assign meanings to an individual’s day to day perceptions and activities and serve in his attempted solutions. |
| How are beliefs formed? |
| Past experience |
| Available information |
| Generalizations |
3. Attitudes
Shakespeare opines “one might smile and smile and yet be a villain” it is not simply a cause of double living as well.
It refers to the way a person feels about and disposed towards some ‘object’. The object could be a physical object or a set of objects (e.g., what’s your attitude towards politics in Nepal?, a specific person (e.g. what’s your thoughts on entrepreneurship in our country?).
- It is evaluative statements or judgment concerning objects, people and events.
- It reflects how an individual feels about something.
- It can be favorable and unfavorable.
- All attitudes embody beliefs.
- It describes people and explain their behavior.
- It is influenced by situation, traits and components.
| Features of Attitudes |
| Attitude is the predisposition of individual to evaluate some object in a favorable or unfavorable manner. |
| The most persuasive phenomenon is ‘attitude’. People at work place have attitudes about lots of topics that are related to them. |
| It is a mental state of readiness’ to be motivated. It is neither behavior nor a cause of behavior. |
| It can also vary in relation to the needs they serve. |
Types of Job related attitudes:
- Job satisfaction
- Job involvement
- Organizational commitment
Attitude formation:
- Experience
- Association (relationship)
- Family
- Peer groups
- Society
- Personality factors
Factors affecting Attitudes:
- Family
- Peers
- Conditioning
- Social Adjustment
- Direct Instruction
- Satisfaction of wants
- Prejudices (Preconceived ideas)
- Tradition and culture
- Media
You may also like Personality || Perception, Personality, and Learning .

Leave a Reply