
Effects of failing to prepare to adjust entries
Effects of failing to organize proper adjusting entries cause net income and the balance sheet to be in error. You are able to see the effect of failing to record each of the major types of adjusting entries on net income and balance sheet items.
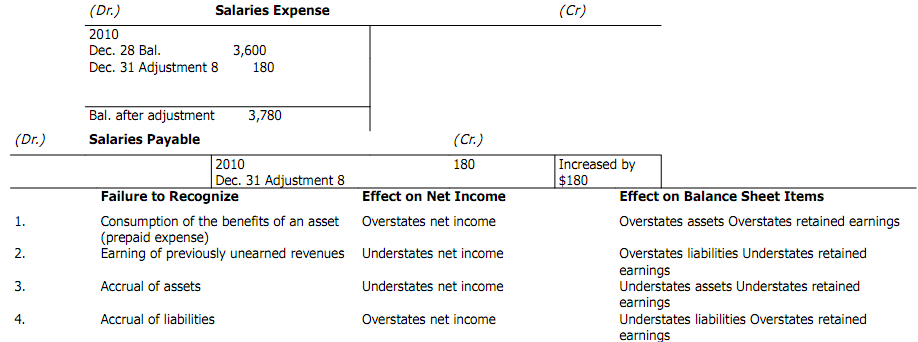
Using Micro Train Company as an instance this section has discussed and illustrated many of the typical entries that companies must make at the end of an accounting period. Afterward, chapters explain other examples of adjusting entries.
On effects of failing, forgetting to make proper depreciation adjustments in your company’s financial records can cause delays in equipment replacement. This can lead to equipment failure due to worn-out components, which can hurt your company’s finances if your business doesn’t have the needed cash to replace the assets.
Reasons for failing to prepare to adjust entries?
Incorrect Capital Expenses Adjustments
Failing to make an appropriate adjustment for depreciation can result in an error with your capital expense deductions for your company’s federal tax return. If the mistake is a simple math miscalculation, or if a company mistakenly forgot to record depreciation when filing, officials with the Internal Revenue Service may simply correct the error without contacting your business and process the tax filing as normal. However, if the error creates a sizable difference in your company’s tax liability, the IRS may begin a formal investigation of your company and audit your tax return to determine how much money your business actually owes the federal government.
Replacing Old Capital Assets
Following your company’s depreciation figures for capital assets, including high-priced equipment, can help you as a business owner determine when to replace equipment and maximize the useful life of these assets. Forgetting to make proper depreciation adjustments in your company’s financial records can cause delays in equipment replacement. This can lead to equipment failure due to worn-out components, which can hurt your company’s finances if your business doesn’t have the needed cash to replace the assets. Productivity may drop dramatically while your business diverts cash from other departments to replace the damaged tools.
Wrong Useful Life Estimates
Determining the rate of depreciation for the majority of capital assets requires your accountants to estimate the useful life of these items. According to WCEQ, useful life refers to the time period the assets are productively in service for your business. Your company’s ability to claim a tax deduction for depreciating capital assets ends at the conclusion of each item’s useful life. According to the IRS, your company accountants use the IRS’ General Depreciation System to determine useful life for the majority of capital assets in your business. Failing to adjust the useful life of your company’s capital assets in accordance with this system could result in tax-documentation errors. Basically, your business could claim tax deductions that it can’t legally take because the assets are past useful life.
Distorted Asset Business Value
The total value of capital assets within your business plays a large role in determining its total worth. If your accountants do not properly depreciate the value of your capital assets – including equipment, office buildings, and vehicles – the total worth of your business distorts. This leads to incorrect financial figures that can confuse potential investors and make it difficult to raise capital. It is unethical at best and illegal at worst for your business accountants to intentionally fail to depreciate assets to artificially increase your company’s total worth.
You may also like Journalizing adjusting entries

Leave a Reply