
Risk Management Process
The risk management process is a framework for the actions that need to be taken. There are five basic steps that are taken to manage risk these steps are referred to as the risk management process. It begins with identifying risks, goes on to analyze risks, then the risk is prioritized, a solution is implemented, and finally, the risk is monitored. In manual systems, each step involves a lot of documentation and administration.
The Five risk management process are:
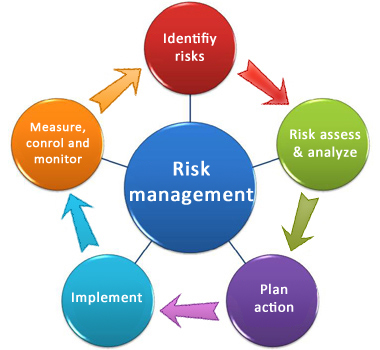
- Identify the Risk
- Analyze the risk
- Evaluate or Rank the Risk
- Treat the Risk
- Monitor and Review the risk
Identify the Risk
The first step is to identify the risks that the business is exposed to in its operating environment. There are many different types of risks – legal risks, environmental risks, market risks, regulatory risks, and much more. It is important to identify as many of these risk factors as possible. In a manual environment, these risks are noted down manually. If the organization has a risk management solution employed all this information is inserted directly into the system. The advantage of this approach is that these risks are now visible to every stakeholder in the organization with access to the system.
Analyze the risk
Once a risk has been identified it needs to be analyzed. The scope of the risk must be determined. It is also important to understand the link between the risk and different factors within the organization. To determine the severity and seriousness of the risk it is necessary to see how many business functions the risk affects. There are risks that can bring the whole business to a standstill if actualized, while there are risks that will only be minor inconveniences in analyzed. In a manual risk management environment, this analysis must be done manually.
Evaluate or Rank the Risk
Risks need to be ranked and prioritized. Most risk management solutions have different categories of risks, depending on the severity of the risk. A risk that may cause some inconvenience is rated lowly, risks that can result in catastrophic loss are rated the highest. It is important to rank risks because it allows the organization to gain a holistic view of the risk exposure of the whole organization.
Treat the Risk
Every risk needs to be eliminated or contained as much as possible. This is done by connecting with the experts of the field to which the risk belongs to. In a manual environment, this entails contacting each and every stakeholder and then setting up meetings so everyone can talk and discuss the issues. The problem is that the discussion is broken into many different email threads, across different documents and spreadsheets, and many different phone calls.
Monitor and Review the risk
Not all risks can be eliminated – some risks are always present. Market risks and environmental risks are just two examples of risks that always need to be monitored. Under manual systems monitoring happens through diligent employees. These professionals must make sure that they keep a close watch on all risk factors. Under a digital environment, the risk management system monitors the entire risk framework of the organization.
You may also like Project Management Life Cycle

Leave a Reply