
Approaches to Probability
The following are the approaches to probability:
- Classical Approach
- Empirical Approach
- Subjective Approach
- Axiomatic Approach
Classical Approach
If there are ‘n’ mutually exclusive and mutually likely cases and ‘m’ of them are favorable to an event ‘E’. Then, the probability of the happening of an event ‘E’ denoted by probability is given by:
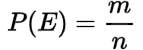
Remarks:
- The probability takes a value between 0 and 1.
- If ‘E’ is an impossible event then, the probability is 0.
- The ‘E’ is sure then P(E)=1.
- The sum of the probabilities of occurrence and non-occurrence is 0 and 1
ie. ![]()
p + q = 1
Laws (Rules) of Probability
1. Additive Law
If A and B are two events with their respective probabilities P(A) and P(B) then the probability of occurrence ![]() at least one of these two events given by:
at least one of these two events given by:
![]()
where P(A U B) is the probability of the simultaneous occurrence of events A and B.
Remarks:
1. If A & B are mutually exclusive event then, ![]()
![]()
2. If A & B & C are 3 events then the ‘P’ of occurrence of at least one of these events is given by:
![]()
If A & B & C are mutually exclusive then, the probability is
![]()
2. Multiplicative Law
If two events A & B are independent then the probability of their simultaneous occurrence is equal to their individual probabilities. If P(A) and P(B) be the probabilities of occurrence of events A & B respectively then the probability of their simultaneous occurrence is given by:
![]()
Remarks:
- If A, B, & C are three independent events then the probabilities of their simultaneous occurrence is given by:
![]()
- If A & B are two dependent events then:
![]()
where,
![]() is the probability of occurrence of event B given that A has already occurred.
is the probability of occurrence of event B given that A has already occurred.
Marginal and Joint Probability
| A | B | Total | |
| C | N1 | N2 | N1 + N2 |
| D | N3 | N4 | N3 + N4 |
| Total | N1 + N2 | N2 + N4 | N |
The probability of each event given by a row or column in the contingency table is called marginal probability.
The marginal probabilities are:
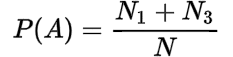
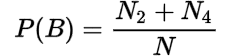
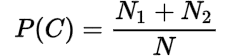
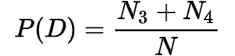
The probability of the joint event whose frequency is given in the cells in the table is called joint probability.
The joint probabilities are:
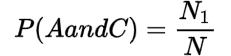
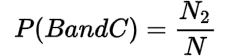
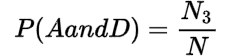
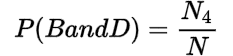
You may also like: Probability and Permutation || Probability

Leave a Reply