
Block Diagram of a Computer
A block diagram of a computer is a diagram of a system in which the principal parts or functions are represented by blocks connected by lines that show the relationships of the blocks which are described below:-
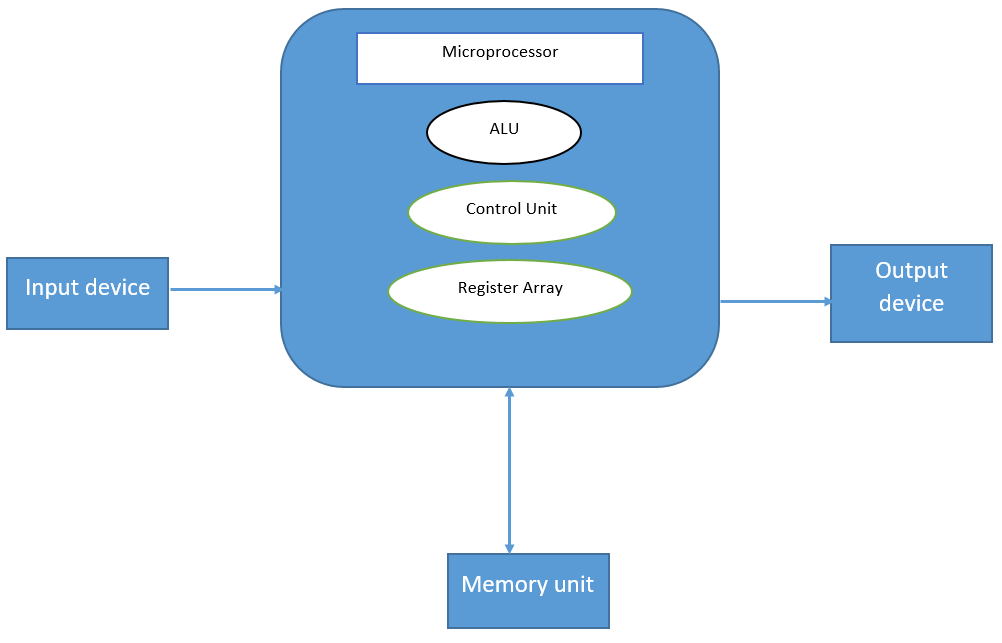
fig:- Block diagram of Computer
- Input
They gather data and convert them into electronic form for use by the computer. Input is the data or instructions entered into the memory of the input device which is any hardware component that allows users to enter data and instructions. Some examples of input devices are keyboards, mouse, joystick, touchpad, touchscreen. - CPU
It is the brain of the computer which executes the instructions, controls the operation of all other components by reading the binary information stored in the memory and provided as input then processes the data and gives output. - Control Unit
A control unit or CU is circuitry that directs operations within a computer’s processor. It lets the computer’s logic unit, memory, as well as both input and output devices know how to respond to instructions received from a program. - Arithmetic and logic unit
Arithematics logic unit is the part of the CPU that handles all the calculations the CPU may need. It does all processes related to arithmetic and logic operations that need to be done on instruction words. It is also known as an integer unit (IU). - Memory unit
A Memory Unit is a collection of storage cells together with associated circuits needed to transfer information in and out of storage. There are two types of memory primary memory and secondary memory.
- Primary memory
This is the category of computer storage often called main memory. It has three functions: Stores all or part of the program that is being executed. Stores the operating system programs that manage the operation of the computer. Holds data that the program is using. - Secondary memory
It is used for relatively long term storage of data outside of the CPU. Secondary storage is non-volatile and retains data even when the computer is turned off. The most technologies are a magnetic disk, optical disk, and magnetic storage. Storage is the place of holding data, instructions, and information for further use. A storage medium is a physical material used for storage. The storage medium is non-volatile contents are retained when power is off. Memory is volatile it holds data and instructions temporarily.6.Output
They display data after they have been processed. The output is the data that has been processed into a useful form. An output device is a hardware component that can convey information to users. An output device that visually conveys information, which is also called a soft copy. Monitor houses display device as separate peripheral the various types of output devices.
You may also like Bus Organization

Leave a Reply