
Range, Quartile Deviation, and Standard Deviation
1. Range
The Range is defined as the difference between the largest item and the smallest item in a set of observations. If L = Largest item and S = Smallest item and their range are denoted by ‘R’ and given by:
R = L – S
Coefficient of Range
The range is of absolute measure. The relative measures corresponding to the range is known as the coefficient of range and is given by:
![]()
2. Quartile Deviation or Semi-interquartile range
The measures of dispersion based on upper quartile and lower quartile is called quartile deviation.
The difference between the upper quartile and lower quartile is called the inter-quartile range.
![]()
Half of the inter-quartile range is called the quartile deviation.
![]()
Coefficient of Quartile Deviation
The relative measure of dispersion based on the upper quartile and lower quartile is called the coefficient of quartile deviation.
![]()
3. Standard Deviation
It is defined as a positive square root of the mean of the square of deviation of items taken from their arithmetic. It is denoted by:
Individual Series
Direct Method
![]()
Shortcut Method
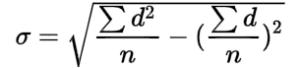
where,
d = X – a
a = Assumed Mean
Discrete Series
Direct Method
![]()
Shortcut Method
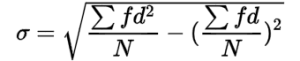
Continuous Series
Step-deviation Method
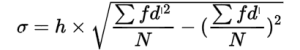
Coefficient of Standard Deviation
The relative measures of dispersion based on the standard deviation is called the coefficient of standard deviation.
![]()
Property of Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation is independent of the change of origin but not of the scale.
Change of origin = (+/-)
Change of scale= ![]()
2. Let n1 and n2 be the sizes and be the mean and σ1 and σ2 be the Standard Deviation of two series and their combined Standard Deviation is denoted by:
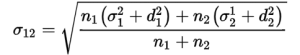
Here,
![]()
![]()
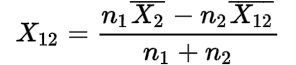
4. Variance
The square of standard deviation is called variance. It is denoted by σ² or µ.
Coefficient of Variance (C.V)
The relative measure of Standard Deviation is multiplied by 100 is called Coefficient of Variance.
![]()
Two series can be compared with the help of the Coefficient of Variance for their variability. Less the value of Coefficient of Variance more will be consistent or uniform and vice versa.
You may also like: Mode || Measures of Central Tendency

Leave a Reply