Methods of forming Class Interval
There are two methods of forming class intervals like exclusive method and inclusive method.
1. Exclusive Method
The formation of the class interval by this method is that if the upper limit of one class is the lower limit of the next class so as to continue without any gap.
Examples:
- 10-20
- 20-30
- 30-40
- 40-50
2. Inclusive Method
The formation of the class interval by this method is that if both lower limits and upper limits are included in a particular way.
Examples:
- 10-19
- 20-29
- 30-39
- 40-49
To convert the class of inclusive type into that of exclusive type.
The correction factor denoted by cf and is given by:
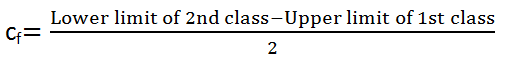
Real Upper Limit = Upper limit + cf
Real Lower Limit = Lower limit – cf
Open-ended Classes
In case of continuous frequency distribution if the lower limit of the first-class or upper limit of the last class isn’t specified or missing those classes are called open-ended classes.
For Example:
Wage No. of Workers
Less than 10 5
10 – 20 10
20 – 30 15
30 – 40 20
40 – 50 8
50 – 60 5
Cumulative frequency distribution
There are two types of cumulative frequency, they are:
- Less than cumulative frequency distribution
- More than cumulative frequency distribution
1. Less than Cumulative Frequency Distribution
Construct the less than the cumulative frequency of the following data:
Wage No. of workers
Less than 10 5
Less than 20 15
Less than 30 30
Less than 40 50
Less than 50 58
Less than 60 63
2. More than Cumulative Frequency Distribution
Q. Construct the more than the cumulative frequency of the following data:
Wage No. of Workers
More than 0 63
More than 10 58
More than 20 48
More than 30 33
More than 40 13
More than 50 5
This is the concepts of Method of forming Class Interval
You may also like Statistics

Leave a Reply