
Managerial Skills
Managerial skills and roles are important topics to be studied in business management. Management skills can be defined as certain attributes or abilities that an executive should possess in order to fulfill specific tasks in an organization. They include the capacity to perform executive duties in an organization while avoiding crisis situations and promptly solving problems when they occur. Management skills can be developed through learning and practical experience as a manager. The skills help the manager to relate with their fellow co-workers and know how to deal well with their subordinates, which allows for the easy flow of activities in the organization.
Simply, managerial skills are the knowledge and ability of the individuals in a managerial position to fulfill some specific management activities or tasks. This knowledge and ability can be learned and practiced. However, they also can be acquired through the practical implementation of required activities and tasks. Therefore, you can develop each skill through learning and practical experience as a manager. Managerial roles and Technical skills, the ability to apply specialized knowledge or expertise is called Managerial skills and roles. Human skills The ability to work with, understand, and motivate other people, both individually and in groups.
Management and leadership skills are often used interchangeably as they both involve planning, decision-making, problem-solving, communication, delegation, and time management. Good managers are almost always good leaders as well. In addition to leading, a critical role of a manager is to also ensure that all parts of the organization are functioning cohesively. Without such integration, several issues can arise and failure is bound to happen. Management skills are crucial for various positions and at different levels of a company, from top leadership to intermediate supervisors to first-level managers.
Types of Management Skills
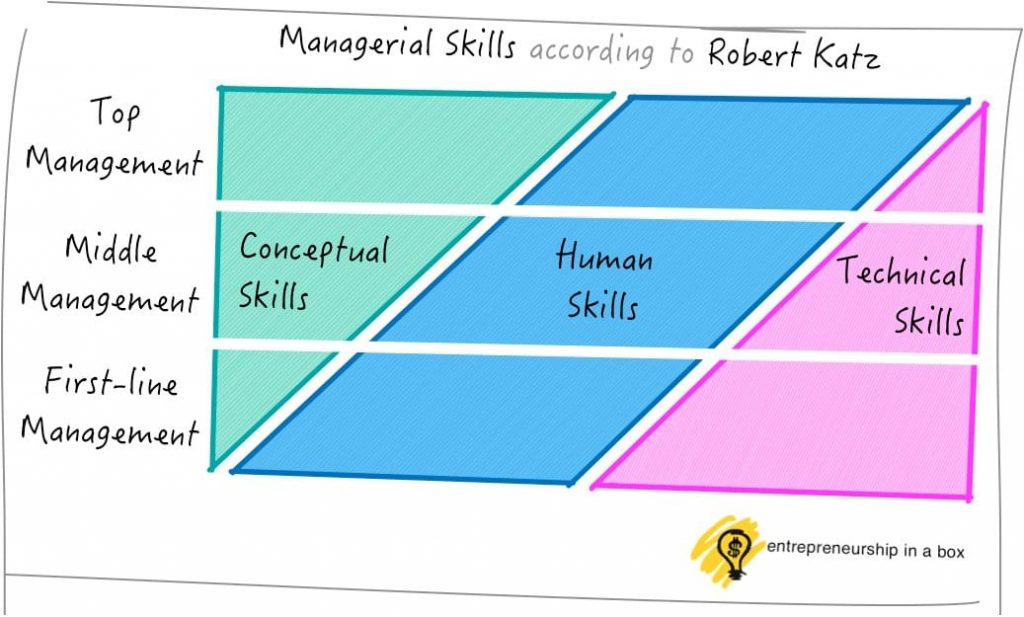
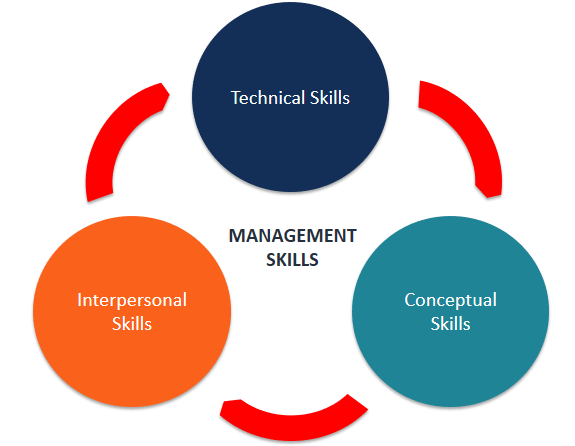
According to American social and organizational psychologist Robert Katz, the three basic types of management skills include:
1. Technical Skills
Technical skills involve skills that give the managers the ability and the knowledge to use a variety of techniques to achieve their objectives. These skills not only involve operating machines and software, production tools, and pieces of equipment but also the skills needed to boost sales, design different types of products and services, and market the services and the products.
2. Conceptual Skills
These involve the skills managers present in terms of the knowledge and ability for abstract thinking and formulating ideas. The manager is able to see an entire concept, analyze and diagnose a problem, and find creative solutions. This helps the manager to effectively predict hurdles their department or the business as a whole may face.
3. Human or Interpersonal Skills
The human or the interpersonal skills are the skills that present the managers’ ability to interact, work or relate effectively with people. These skills enable the managers to make use of human potential in the company and motivate the employees for better results.
Managerial Roles
Another way to approach what managers do is to consider the role they play in an organization. The functions of management make clear what managers do, whereas the management roles indicate how they do it. A role is defined as “the expected behavior for a certain status or position.” A manager’s position in an organization’s structure makes it both necessary and possible to perform these roles.
In 1973, Henry Mintzberg – a Canadian academic and author on business and management published a book called ‘The Nature of Managerial Work’. A classic now, Mintzberg based his book on data derived from the time diaries of male executives.
Managerial Roles
For better understanding, Mintzberg categorized all activities into ten managerial roles performed over the course of a day. These are as follows:
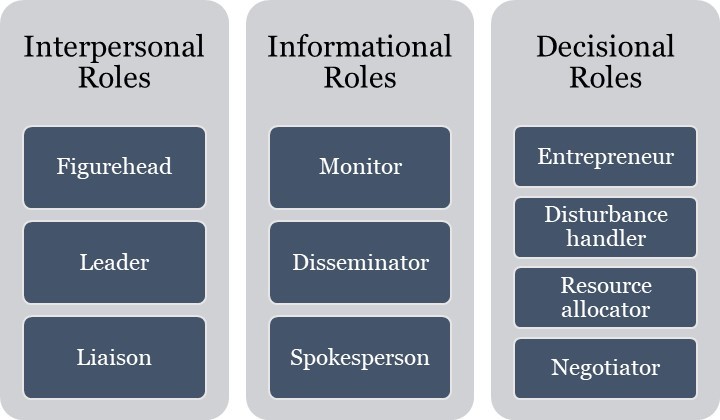
1. Interpersonal Roles
- Figurehead – includes symbolic duties which are legal or social in nature.
- Leader – includes all aspects of being a good leader. This involves building a team, coaching the members, motivating them, and developing strong relationships.
- Liaison – includes developing and maintaining a network outside the office for information and assistance. 2
2. Informational Roles
- Monitor – includes seeking information regarding the issues that are affecting the organization. Also, this includes internal as well as external information.
- Disseminator – On receiving any important information from internal or external sources, the same needs to be disseminated or transmitted within the organization.
- Spokesperson – includes representing the organization and providing information about the organization to outsiders.
3. Decisional Roles
- Entrepreneur – involves all aspects associated with acting as an initiator, designer, and also an encourager of innovation and change.
- Disturbance handler – taking corrective action when the organization faces unexpected difficulties that are important in nature.
- Resource Allocator – being responsible for the optimum allocation of resources like time, equipment, funds, and also human resources, etc.
- Negotiator – includes representing the organization in negotiations that affect the manager’s scope of responsibility.
The Important Features of these managerial roles:
- These roles are interconnected. Neglecting one would affect the job performance of the manager.
- For effective teamwork, each of these roles must be performed consistently.
- Performing all these roles simultaneously demands managing time effectively. Otherwise, one role would be ignored or forgotten at the cost of another role.
You may also like Emerging Issues and Challenges in Management

Leave a Reply