
Movement along a Supply Curve and Shift in Supply Curve
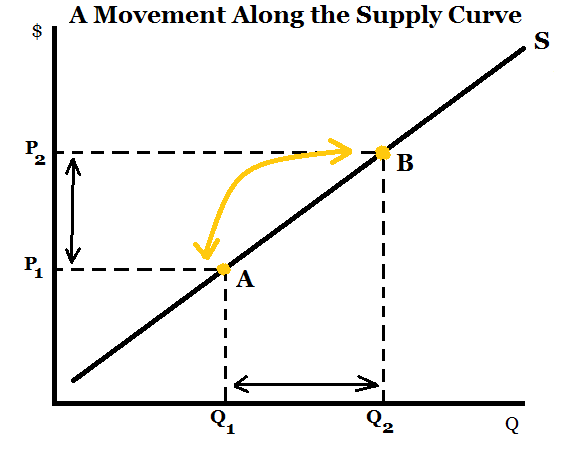
1. Movement along a Supply Curve (Change in Quantity Supplied)
A change in the quantity supplied refers to the movement from one point to another along a fixed supply curve. Such movement indicates a change in the price of the specific product under consideration. The rise in the quantity supplied due to the rise in price, other things being equal, is known as an extension of supply. On the other hand, the fall in the quantity supplied due to the fall in price, other things being equal, is known as the contraction of supply. It is shown by the following schedule:
| Price | Quantity Supplied |
| 20 | 200 |
| 30 | 300(Extension in Supply) |
| 10 | 100(Contraction in Supply) |
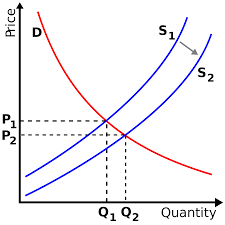
2. Shift in Supply Curve (Change in Supply)
A change in supply is involved when the entire supply curve shifts. An increase in supply shifts the supply curve to the right; a decrease in supply shifts it to the left. The cause of change in supply is a change in one or all the determinants of supply. In other words, a shift occurs when the producers are willing to offer more or less of a commodity due to the change in other determinants of supply except for the price. It is shown in the following supply schedule and curves:
| Quantity supplied | |||
| Price (Rs) | Initial | When cost Rises | When Cost Falls |
| 10 | 100 | 20 | 200 |
| 20 | 200 | 100 | 400 |
| 30 | 300 | 150 | 600 |
A change in one or more of the determinants of supply, except the price of a commodity such as resource prices, the prices of other goods, productive techniques, taxes and subsidy, development of infrastructures and the price exceptions will cause a change in the supply.
You may also like: Factor causing Shift in Supply Curve

Leave a Reply