
Price and output determination-Perfect Competition
The Price and output determination-Perfect Competition is explained below.
Perfect competition: A perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been theoretically demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every product or service, including labour, equals the quantity demanded at the current price.
Characteristics of perfect competition:-
- Large numbers of sellers and buyers
- Homogeneous products
- Free entry and exit of firms
- Price taker
- AR and MR are constant
- No selling cost
Price determination- Market forces of demand-supply determine price of the product at market due to which firms under perfect competition are considered as a price taker.
Output determination- Output is determined on the basis of the following conditions.
- MR=MC
- MC must cut MR from below.
Profit situation of a firm:
- If AR>AC, firms are in abnormal profit / supernormal profit.
- If AR=AC, firms are in normal profit.
- If AR<AC, firms are in loss/negative profit.
Equilibrium of a firm can be shown by the help of the following diagram:
a) Short-run equilibrium
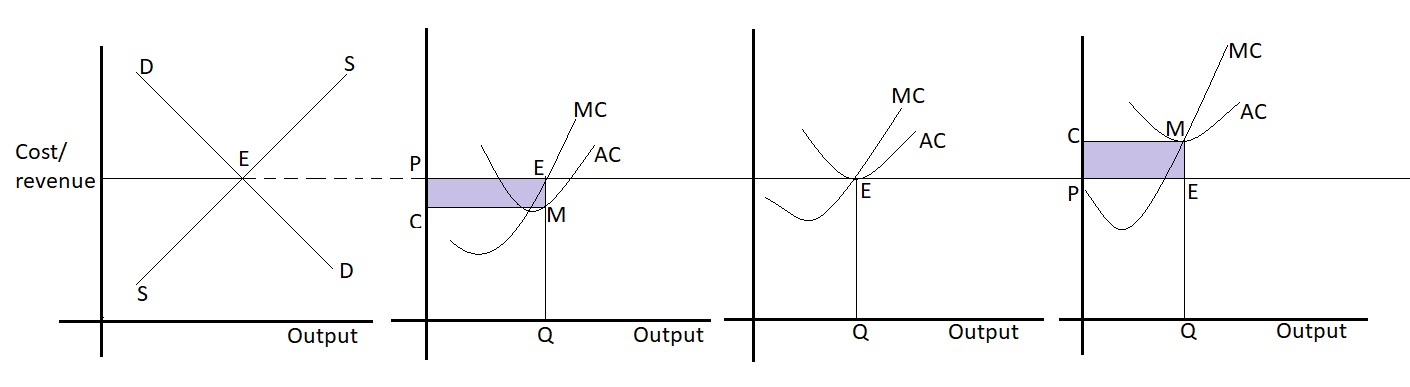
In the diagram, the market determines P price for the product at the existing price.
Firm ‘A’ is in
TR= P × Q
= OP × OQ
= OQEP
TR= AC × Q
= OC × OQ
= OCMQ
profit= TR – TC
= PEMC
The firm is in supernormal profit.
Firm ‘B’ is in
TR = P × Q
= PEOQ
TC = AC × Q
= PEOQ
profit = TR – TC
=0
The firm is in normal profit.
Firm ‘C’ is in
TR= P× Q
= OPEQ
TC = AC × Q
= OCMQ
profit= TR-TC
= -CMEP
The firm is in the loss.
b) Long-run equilibrium
In long-run all abnormal profit and losses are converted into normal profit because there are large numbers of sellers and there are free entry and exit of a firm.
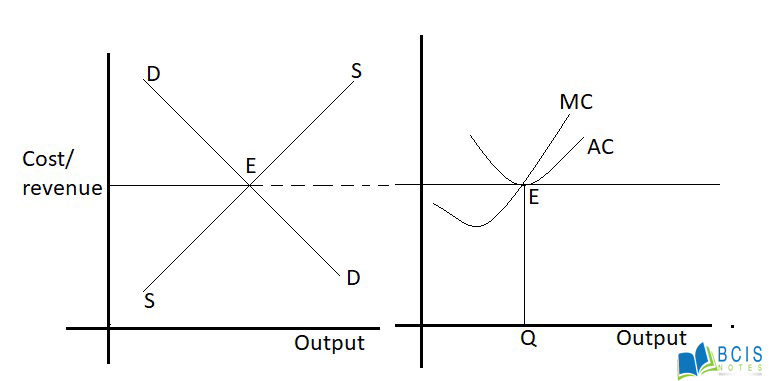
Therefore the Price and output determination- Perfect Competition is explained above.
You may also like Price and output determination (TR-TC Approach)

Leave a Reply