
The basic economic issues arise from scarcity and choice.
Scarcity
Scarcity refers to the limited supply of productive resources in relation to their demand. A resource is said to be scarce if the demand for it exceeds its supply. It is the condition in which resources are not available in an adequate amount to satisfy all the wants and needs of the people. It is the heart of all the economic problems. As human wants are unlimited and resources available are limited, scarcity is perpetual and universal.
Choice
Choice refers to a selection of highly urgent wants from unlimited wants in order to achieve an optimum allocation of limited resources. As the resources are scarce the society must be able to decide which want will be satisfied and which will not. Maximum possible satisfaction should be obtained from the utilization of productive resources that are available in a useful manner. Our choice has to be such that most of our wants be satisfied.
Problems of scarcity and choices
The scarcity of resources gives rise to the fundamental economic problem of choice. As the society cannot produce enough goods and services with limited resources for unlimited wants it has to make the choices. This is why a decision to produce one good requires less of producing other goods. The economic problem that arises from the scarcity and choice should be solved in one way or the other. Thus, the economic problem is common to both the rich and poor countries. However, the nature of the economic problem is different.
Allocation of Resources
The allocation of resources is defined as the process of selection of resources and their proper utilization. As various resources are required to produce goods and services but the resources are scarce so we have to study what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce and how to maintain economic growth.
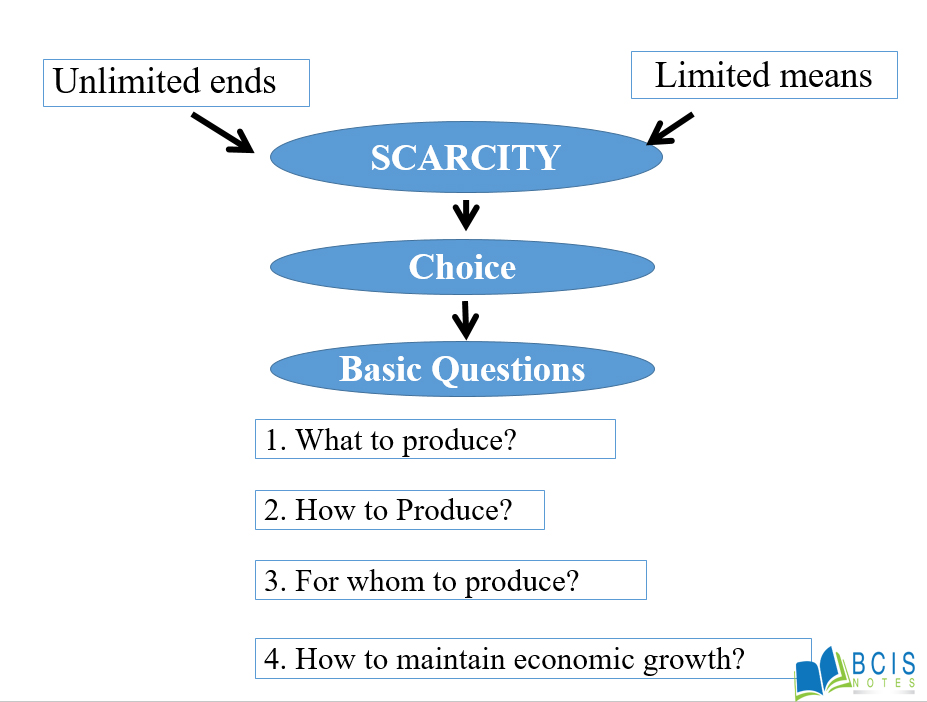
Figure- Basic economic issues
- What to produce- What to produce refers to the problem of production. Due to the cause of limited resources, a firm must decide what to produce. For example, if a society wants to start a biscuits factory, it must have a clear idea about the biscuit it wants to manufacture. If it wants to produce cream biscuit then it should check whether the cream, labor capital, land, and entrepreneurship is available for the production or not, can there be any problems in the off-season, etc.
- How to produce- How to produce refers to the way in which resources or the inputs are organized to produce goods and services that consumer wants. A firm must understand the best way to produce any good. For this, it should use the best resources for production and use such technology that would use the resources in the best manner. Hence, it deals with the technique of production.
- For whom to produce- A society must decide the target for whom it wants to produce its goods. As some are poor and some are rich, society must decide which group it wants to target. If it produces at a lower cost then the poor people can use it. If the output price is very high then only rich people can get it. Therefore, it deals with the way the output is distributed among the members of society.
- How to maintain economic growth- How to maintain economic growth deals with how to increase the productive capacity of the economy. The economic growth rate affects the production of society and the overall demand of social members. If the growth rate is negative then the demand will be lower and production should be limited.
Production Possibility of Curve
Production Possibility curve is also known as Production Possibility frontier or Transformation Curve. It can be defined as the locus of points that represents the various optimal combination of goods and services which can be produced efficiently by the economy with the full utilization of given resources and technology. It is used to explain the basic economic concepts: Scarcity, Choices and Opportunity cost.
Assumptions:-
- Available resources are fully and efficiently utilized.
- The number of resources available is fixed.
- The state of technology does not change throughout the production.
- Perfect mobility of factor of production from one use to another.
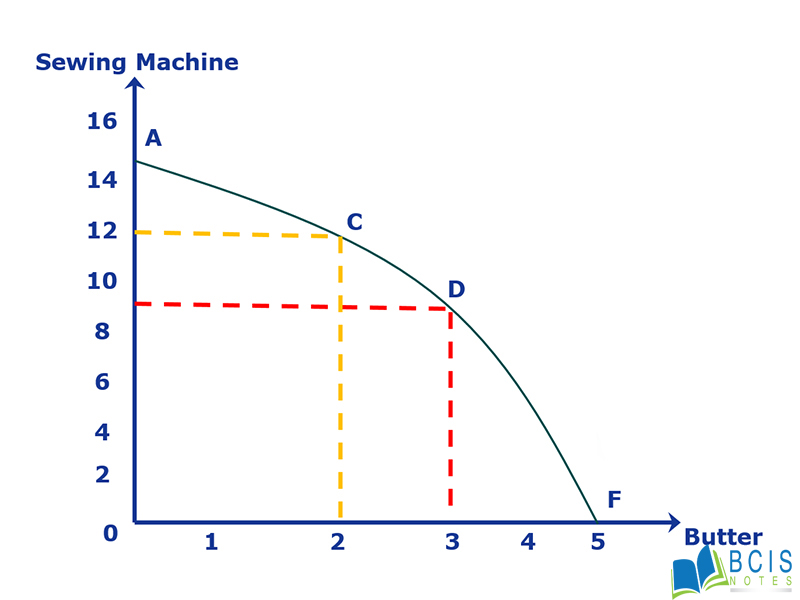
Figure- Production possibility Curve
In this figure, we measure the sewing machine and butter in the y-axis and x-axis respectively. The various points on the boundary of PPC (A, C, D and F points in the diagram) represent the combination of goods that can be produced using the resources and technology that are available.
From the above graph, we can know that if it allocates all its resources to the sewing machine, it will produce at Point A. Similarly when it allocates all its resources to butter, it will produce at Point F. Here we can learn that if we want to produce more sewing machine we have to reduce the output of butter. Thus a PPC tells us that we can produce any commodity more by reducing some of the other and vice versa.
You may also like Concept of Market Economy

Leave a Reply