
Operation of Process
The operations of the process carried out by an operating system are primarily of two types:
- Process Creation
- Process termination
i. Process Creation
Process creation is the task of creating new processes. There are different situations in which a new process is created. There are different ways to create a new process. A new process can be created at the time of initialization of the operating system or when the system calls such as fork () are initiated by other processes. The process, which creates a new process using system calls, is called the parent process while the new process that is created is called the child process. The child processes can create new processes using system calls. A new process can also create by an operating system based on the request received from the user.
The process creation is very common in running a computer system because corresponding to every task that is performed there is a process associated with it. For instance, a new process is created every time a user logs on to a computer system, an application program such a MS Word is initiated, or when a document printed.
ii. Process termination
Process termination is an operation in which a process is terminated after the execution of its last instruction. This operation is used to terminate or end any process. When a process is terminated, the resources that were being utilized by the process are released by the operating system. When a child process terminates, it sends the status information back to the parent process before terminating. The child process can also be terminated by the parent process if the task performed by the child process is no longer needed. In addition, when a parent process terminates, it has to terminate the child process as well as become a child process cannot run when its parent process has been terminated.
The termination of a process when all its instruction has been executed successfully is called normal termination. However, there are instances when a process terminates due to some error. This termination is called abnormal termination of a process.
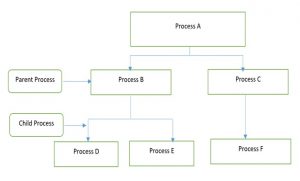
The above figure shows the hierarchical structure of processes.
A. Concurrent processing
Concurrent processing is a computing model in which multiple processors execute instructions simultaneously for better performance. Tasks are broken down into subtasks that are then assigned to separate processors to perform simultaneously, instead of sequentially as they would have to be carried out by a single processor. Concurrent processing is sometimes said to be synonymous with parallel processing.
B. Parallel Processing
Parallel processing, one form of multiprocessing, is a situation in which two or more processors operate in unison. Two or more CPUs are executing instructions simultaneously. The Processor Manager has to coordinate the activity of each processor as well as synchronize cooperative interaction among the CPUs. There are two primary benefits to parallel processing systems:
- Increased Reliability
a. The availability of more than one CPU.
b. If one processor fails, then the others can continue to operate and absorb the load. - Faster processing
The increased processing speed is often achieved because sometimes Instructions can be processed in parallel, two or more at a time in one of several ways:
a. Some systems allocate a CPU to each program or job.
b. Others allocate a CPU to each working set or parts of it
c. Subdivide individual instructions so that each subdivision can be processed simultaneously.
You may also like: Introduction to Process.

Leave a Reply