
Introduction to Data Communication
Data communication refers to the exchange of data between a source and a receiver via a form of transmission media such as a wire cable. It is said to be local if communicating devices are in the same building or a similarly restricted geographical area.
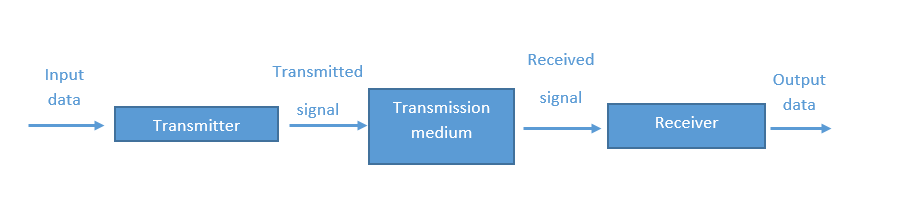
fig:- Simple Data Communication System
Block diagram
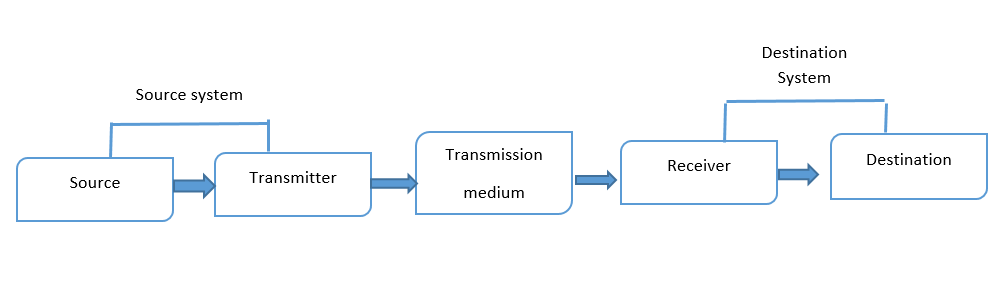
fig:- Block diagram
The above figure shows the basic block diagram of a typical data communication system. This can further be broken down into three;
- the source system,
- the transmission system,
- destination system.
- The Source System:-
The source generates the information or data that will be transmitted to the destination. Popular forms of information include text, numbers, pictures, audio, video or a combination of any of these. - Transmitter:-
The transmitter is a device used to convert the data as per the destination requirement. For example, a modem converts the analog (telephonic) signal to digital (computer) signals and alternatively digital to analog. - Transmission medium:-
The transmission medium is the physical path by which data travels from the transmitter to the receiver. For Example, of such channels is copper wires, optical fibers, and wireless communication channels, etc. - Receiver:-
This receives the signals from the transmission medium and converts it into a form that is suitable to the destination device. For example, a modem accepts an analog signal from a transmission channel and transforms it into a digital bitstream which is acceptable by the computer system. - Destination:-
It is simply a device for which source device sends the data.
Components
- Message:
The message is the information (data) to be communicated. Popular forms of information include text, numbers, pictures, audio, and video. - Sender:
The sender is the device that sends the data message. It can be a computer, workstation, telephone handset, video camera, and so on.
- Receiver:
The receiver is the device that receives the message. It can be a computer, workstation, telephone handset, television, and so on.
- Transmission medium:
The transmission medium is the physical path by which a message travels from sender to receiver. Some examples of transmission media include twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, and radio waves. - Protocol:
A protocol is a set of rules that govern data communications. It represents an agreement between the communicating devices. Without a protocol, two devices may be connected but not communicating, just as a person speaking French cannot be understood by a person who speaks only Japanese.

Leave a Reply